Lab 4: Seismic Deconvolution
The
aim of seismic deconvolution is to increase the vertical resolution of the data
by compressing the source wavelet (to a zero-phase spike, if possible) This is
known as spiking deconvolution. Not only that, seismic deconvolution also aims
to attenuate noise such as multiples elimination. For this, we need to define
the seismic convolution model.
To
perform spiking deconvolution, we need to set 3 parameters namely:
a) Auto-correlation window (w)
b) Filter length (N)
c) Percent pre-whitening
1. Call
and display for seismic shot gather no. 4-6 as shown in figure below before
applying spiking deconvolution.
Figure 1
Figure 2: Shot
gathers:4,5 and 6 before applying spiking deconvolution
2. Performing
Auto-correlation
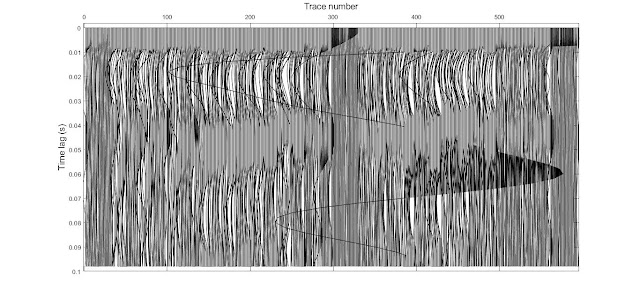
Figure 3:
Auto-correlograms of shot gather number 4,5 and 6.
3. Applying
spiking deconvolution
The
aim of spiking deconvolution is to compress the source wavelet into zero-phase
spike of zero width. This means that we are eliminating the effect of source
wavelet and only remain the Earth’s reflectivity in the seismogram. Based on
Figure 4, it can be seen that the data became spiker.
Figure 4: Shot gather 4,5 and
6 after applying spiking deconvolution
4. Analyze
further in the spectrum domain via the power spectral density of the average
traces
Figure 5: PSD of the average
trace of shot gathers 4,5 and 6 before and after spiking deconvolution
5. Apply
AGC with window length of 0.5 s to the deconvolved data as in Figure 6. AGC is
applied to compensate for the lost amplitudes after deconvolution
Figure 6: Shot gather
4,5, and 6 after applying deconvolution and instantaneous AGC







Comments
Post a Comment